Kitchen Gas Cooking Appliance Parts Gas Regulator plays a vital role in home kitchen gas appliances. It ensures safe and efficient operation of equipment by regulating and stabilizing gas pressure. So, how is the adjustment process of Kitchen Gas Cooking Appliance Parts Gas Regulator implemented?
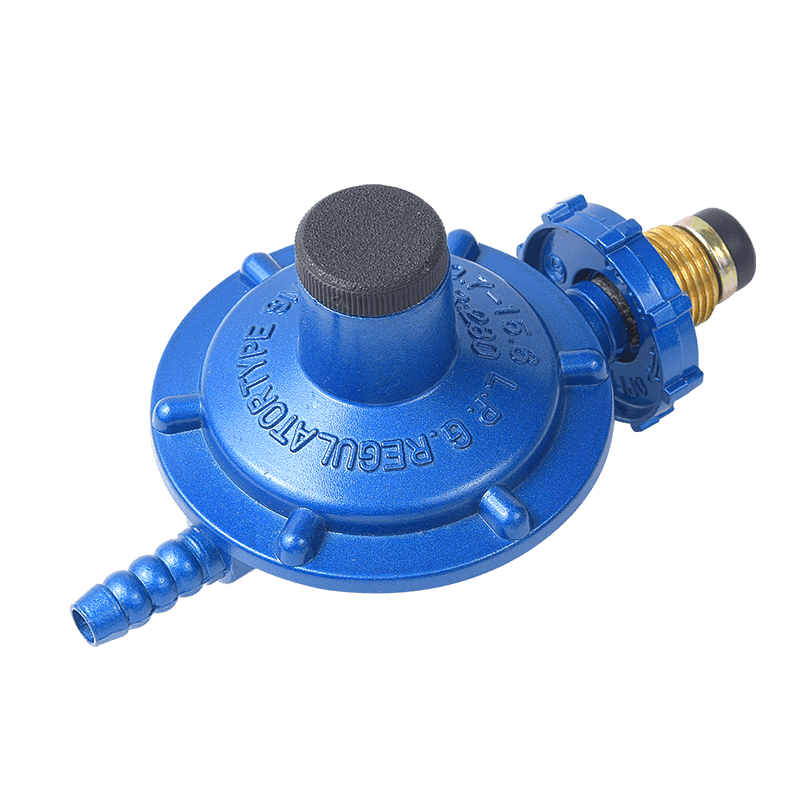
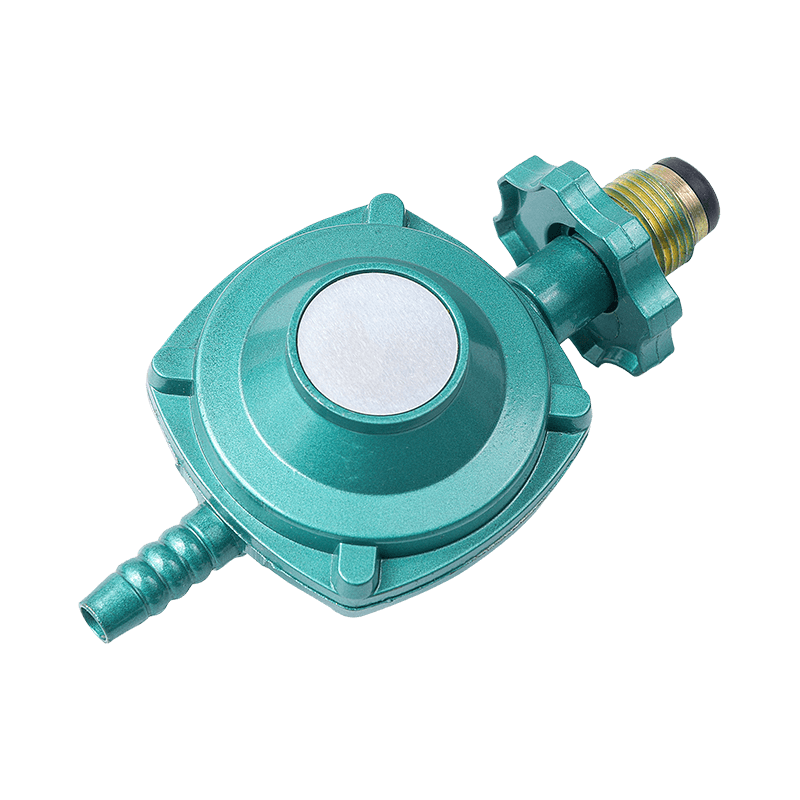
Kitchen Gas Cooking Appliance Parts The internal structure of the Gas Regulator is relatively complex, but its core components mainly include the air inlet, regulating valve, diaphragm, spring and air outlet. Each component has its specific function and works together to regulate and control gas pressure.
High-pressure gas enters the regulator through the air inlet. The air inlet is usually connected to the gas supply pipe, and it must be ensured that the connection is tight and there is no air leakage.
The regulating valve is the core component of Kitchen Gas Cooking Appliance Parts Gas Regulator, which controls the gas flow by opening and closing. The opening of the regulating valve determines the amount of gas entering the regulator, which directly affects the output pressure.
The diaphragm is a flexible component that senses pressure changes. When the gas pressure changes, the diaphragm moves accordingly and adjusts the opening of the regulating valve through a mechanical linkage.
The spring provides a reaction force that works together with the diaphragm to ensure that the regulator can operate stably under different pressure conditions. The stiffness and preload force of the spring determine the output pressure range of the regulator.
The adjusted gas flows out from the gas outlet and enters the cooking equipment. The air outlet is usually connected to the gas port of the device, and it also needs to be ensured that there is no air leakage.
The adjustment process of Kitchen Gas Cooking Appliance Parts Gas Regulator can be divided into the following key steps:
High-pressure gas enters the regulator's air inlet from the gas supply pipe. At this time, the gas pressure is high, far exceeding the needs of the cooking equipment.
When high-pressure gas enters the regulator and passes through the regulating valve, the diaphragm senses changes in gas pressure. When the diaphragm is pressurized, it will move, and this displacement will reflect the current gas pressure level.
The displacement of the diaphragm is transmitted to the regulating valve through a mechanical linkage. When the diaphragm is pushed by high pressure, the regulating valve will gradually close to reduce the gas flow; conversely, when the pressure is low, the diaphragm will rebound and the regulating valve will gradually open to increase the gas flow.
As the regulating valve is adjusted, the amount of gas entering the regulator changes. The pressure inside the regulator gradually stabilizes, and the displacement of the diaphragm also tends to balance. At this time, the reaction force of the spring and the force of the diaphragm reach a balanced state, and the regulating valve remains in a relatively stable position.
The adjusted low-pressure gas flows out from the gas outlet and enters the cooking equipment. At this time, the gas pressure is stable within the range required by the equipment, ensuring that the equipment works safely and efficiently.
An important feature of the Kitchen Gas Cooking Appliance Parts Gas Regulator is its automatic adjustment mechanism. This mechanism relies on the interaction of the diaphragm and the spring, and can automatically adjust the opening of the regulating valve under different gas pressure conditions to ensure that the output pressure is always stable. For example, when the gas supply pressure fluctuates, the regulator can respond quickly and maintain the stability of the output pressure through the adjustment of the diaphragm and regulating valve.
In practical applications, it is crucial to properly install and maintain the Kitchen Gas Cooking Appliance Parts Gas Regulator. First, you must ensure that the connections between the regulator and gas pipes and equipment are tight and leak-free. Secondly, regularly check the working status of the regulator and remove surrounding dust and impurities to avoid affecting its normal operation.

 EN
EN English
English 中文简体
中文简体